Which Best Describes the Boundary Layer
How thick is the concentration boundary layer in the air. For radiative energy incident on a surface reflectivity absorptivity transmissivity 1.
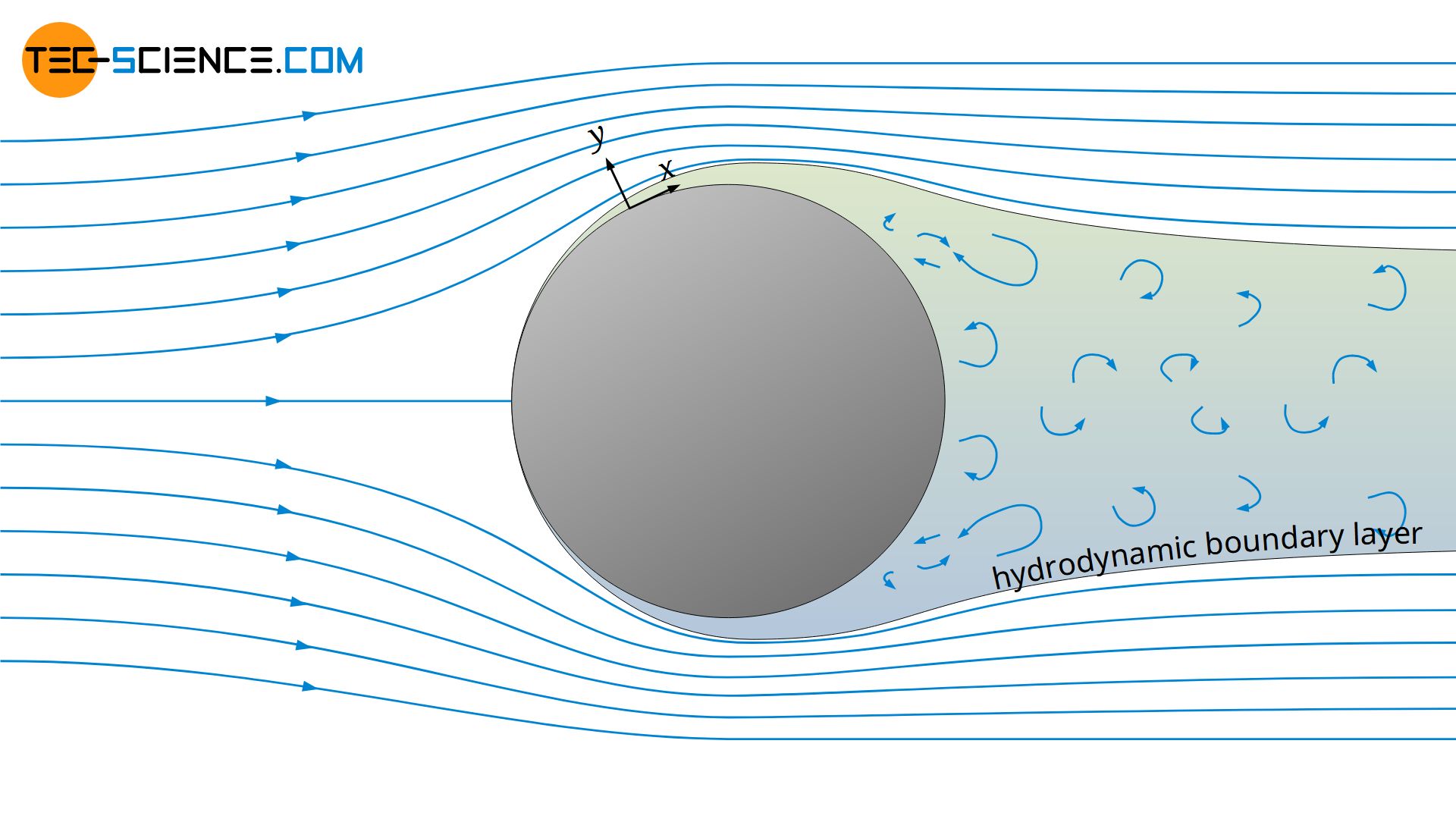
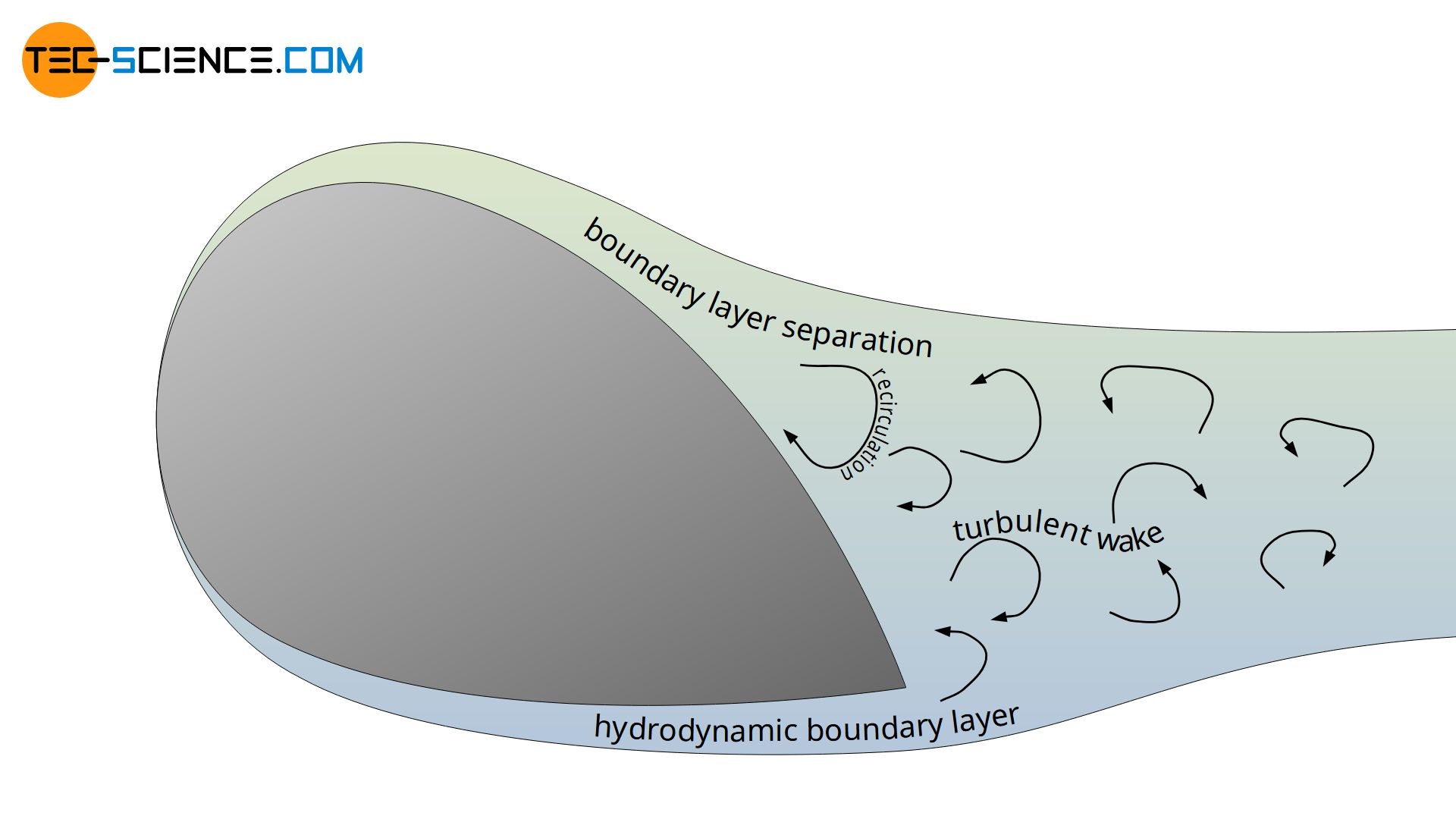
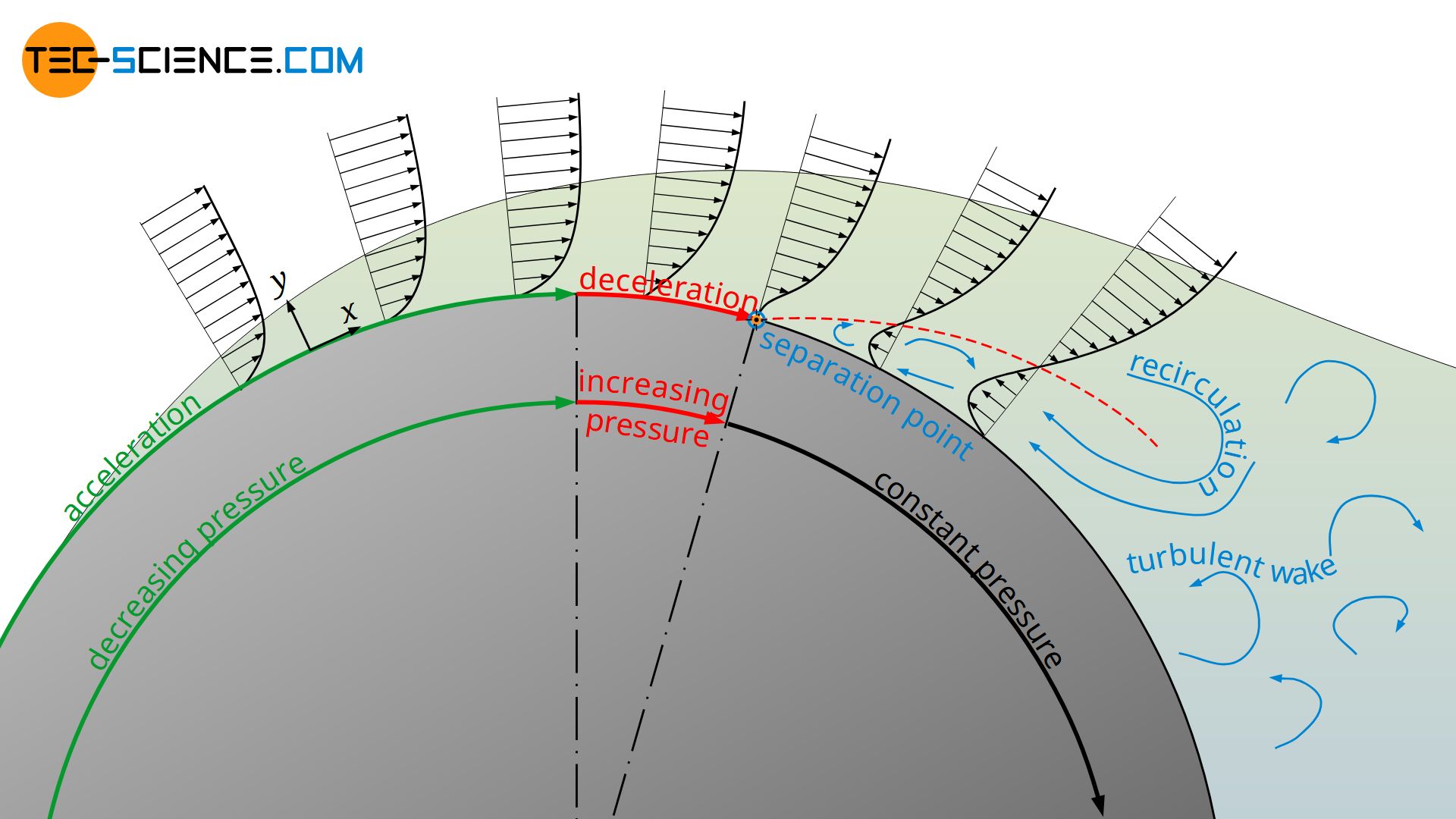
Flow Separation Boundary Layer Separation Tec Science
The following second-order differential equation describes the motion of a certain mass connected to a spring and damper.
. Where Rex is the Reynolds number based on the length of the plate. Starting point are the NavierStokes equations for steady two-. A range of velocities exists across the boundary layer from maximum to zero provided the fluid is in contact with the surface.
Coarse sediment mixed with uniform Cretaceous mud in Texas. The energy thickness δ is defined as the thickness of the flow moving at the free stream velocity having the energy equal to the deficiency of energy in the boundary layer region. Noun a region of fluid such as air moving relative to a nearby surface such as that of an airplane wing that is slowed by the viscosity of the fluid and its adhesion to the surface.
This is a slightly tricky question so think about it carefully in the context of the reading. This concept would eventually lay down the foundations of modern aeronautical engineering and today is at the base of most modern calculations of skin friction heat transfer and flow separation. General term used to describe the atmospheric layer up to about 100 m above the ground surface where the air flow is largely conditioned by the frictional effects of the.
The boundary layer is a thin zone of calm air that surrounds each leaf. A thick boundary layer can reduce the transfer of heat CO 2 and water vapor from the leaf to the environment. The boundary layer is defined as the region where the local velocity values are less or equal than the 99 value or other reference value of the freestream value.
Questions of race. The boundary layer is the portion of fluid adjacent to the surface of an object around which the fluid is flowing. Outside these areas non-viscous equations can be used.
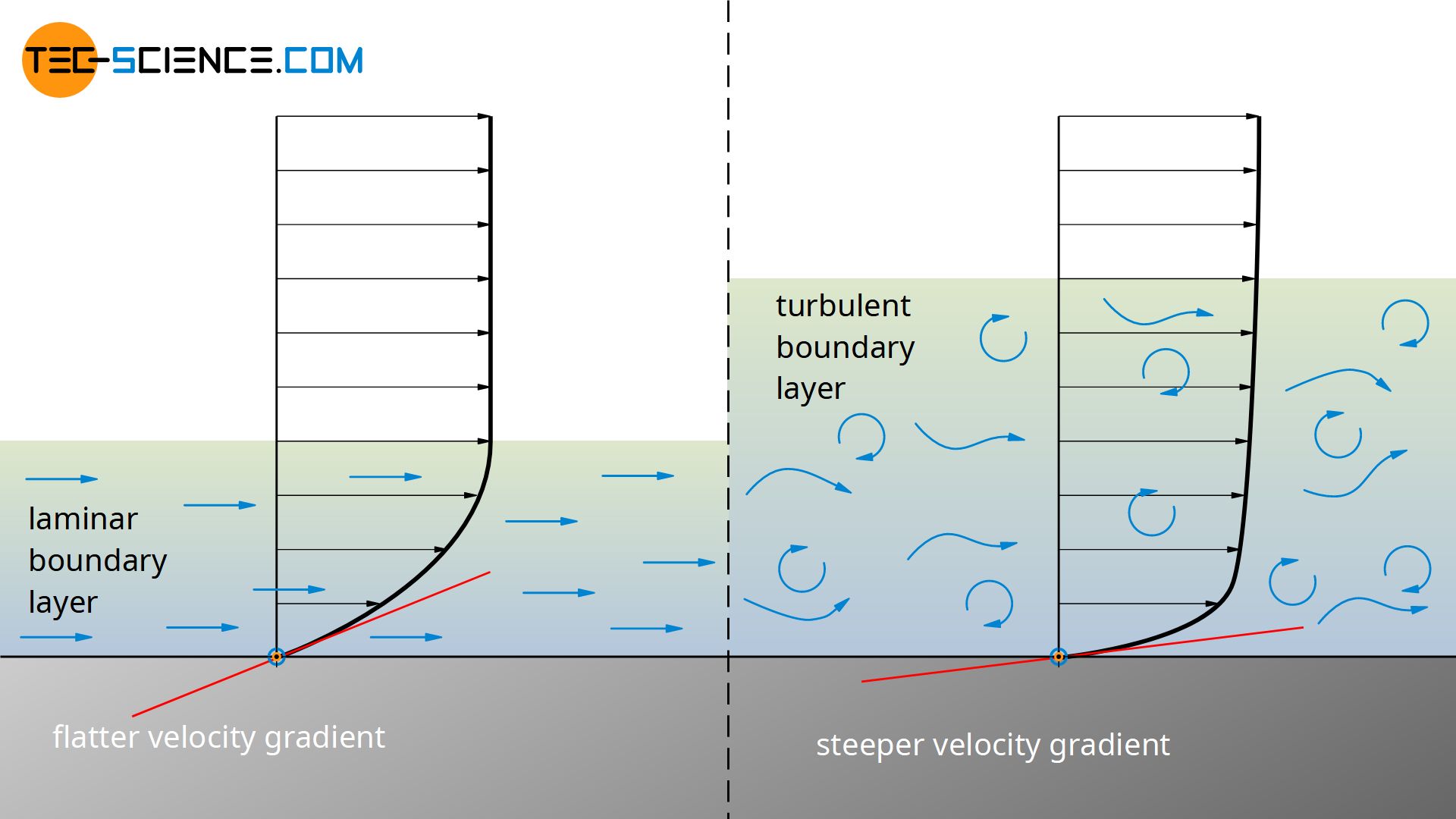
Boundary layer in fluid mechanics thin layer of a flowing gas or liquid in contact with a surface such as that of an airplane wing or of the inside of a pipe. For laminar boundary layers over a flat plate the Blasius solution of the flow governing equations gives. Answer Advertisement Advertisement kid95469 kid95469 The laminar boundary is a very smooth flow while the turbulent boundary layer contains swirls or eddies The laminar flow creates less skin.
Boundary layers are thinner. Lack of an isotope of plutonium in the K-T boundary layer. Energy thickness may be conceived as the transverse distance by which the boundary layer.
The general fluids equations had been known for many years but solutions to the equations did not properly describe observed flow effects like wing stalls. The theory which describes boundary layer effects was first presented by Ludwig Prandtl in the early 1900s. It is also possible to have boundary layers for other flow variables eg.
False - high level of iridium was only one piece of evidence. Which wavelength range best describes thermal radiation. The thickness of the boundary layer influences how quickly gasses and energy are exchanged between the leaf and the surrounding air.
Boundary Layer Thickness. The boundary layer is the region of a flow close to a surface where there is a gradient of velocity between zero at the wall and the free-stream velocity v which is caused by viscosity and the no-slip condition. However the idea of partitioning the flow into an inviscid mainstream and viscid boundary layer is still essential for fundamental insights into basic aerodynamics.
My best wishes to Ukraina and Ukrainians. In 1904 Ludwig Prandtl introduced an approach to understanding and analyzing flows around bodies that produced a massive breakthrough. 10-1 to 102 microns.
Laminar boundary layers can be loosely classified according to their structure and the circumstances under which they are created. One simple example that nicely demonstrates the physics of boundary layers is the problem of flow over a flat plate. We define the thickness of the boundary layer as the distance from the wall to the point where the velocity is 99 of the free stream velocity.
The fluid in the boundary layer is subjected to shearing forces. These terms are only of interest in local areas of high shear boundary layer wake. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Temperature or scalar concentration. The thickness of the boundary layer influences how quickly gasses and energy are exchanged between the leaf and the surrounding air. Air is viscous so to move one air layer with respect to other is necessary to apply a force.
Prandtls boundary layer is not the only physically interesting boundary layer and the aim of this section is to describe other types of viscous boundary layers which appear in particular in Meteorology and in MHD the basic example being the Ekmann layer. Laminar and turbulent boundary layers. High levels of iridium in the K-T boundary layer.
At the interface between a solid surface and a fluid a thin fluid layer that is static because of friction between molecules of the fluid and the solid. The Adventure of Geography. A thick boundary layer can reduce the transfer of heat CO2 and water vapor from the leaf to the environment.
Differences in foraminifera fossils above and below the K-T boundary layer. The layer is the boundary between the object and the free-flowing fluid. Prandtls boundary layer is not the only physically interesting boundary layer and the aim of this section is to describe other types of viscous boundary layers which appear in particular in Meteorology and in MHD the basic example being the Ekmann layerNamely in meteorology or oceanography.
Which of the following best describes the flow in the boundary layer. 3y 3y 75y 10 sin51 The. Through distance δ ½ ρbδU0xU02 ½ ρbδxU03.
Boundary layer 1. Namely in meteorology or oceanography. The speed at wall is zero.
The boundary layer is a thin zone of calm air that surrounds each leaf. Grenier in Handbook of Mathematical Fluid Dynamics 2005 41 Introduction. The thin shear layer which develops on an oscillating body is an example of a Stokes boundary layer while the Blasius boundary layer refers to the well-known similarity solution near an attached flat plate held in an oncoming unidirectional flow and FalknerSkan b.
The audio illustrations photos and videos are credited beneath the media asset except for promotional images which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. Grenier in Handbook of Mathematical Fluid Dynamics 2005 41 Introduction. - 14921392 rochelle1664 rochelle1664 19052021 English.
We begin with the derivation of the equations that describe the ow in shear layers like boundary layers and wakes.
Flow Separation Boundary Layer Separation Tec Science

Plate Tectonics Vocabulary And Lesson Activities Geography Plate Tectonics Lessons Activities Homeschool Elementary
Comments
Post a Comment